 | Info
Sheets |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
 | Out-
side |
| | | | |
|
| | | | | |  | Searchterm 'Coil' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
In parallel MR imaging, a reduced data set in the phase encoding direction(s) of k-space is acquired to shorten acquisition time, combining the signal of several coil arrays. The spatial information related to the phased array coil elements is utilized for reducing the amount of conventional Fourier encoding.
First, low-resolution, fully Fourier-encoded reference images are required for sensitivity assessment. Parallel imaging reconstruction in the Cartesian case is efficiently performed by creating one aliased image for each array element using discrete Fourier transformation. The next step then is to create an full FOV image from the set of intermediate images.
Parallel reconstruction techniques can be used to improve the image quality with increased signal to noise ratio, spatial resolution, reduced artifacts, and the temporal resolution in dynamic MRI scans.
Parallel imaging algorithms can be divided into 2 main groups:
Image reconstruction produced by each coil ( reconstruction in the image domain, after Fourier transform): SENSE ( Sensitivity Encoding), PILS (Partially Parallel Imaging with Localized Sensitivity),
ASSET.
Reconstruction of the Fourier plane of images from the frequency signals of each coil ( reconstruction in the frequency domain, before Fourier transform): GRAPPA. Additional techniques include SMASH, SPEEDER™,
IPAT (Integrated Parallel Acquisition Techniques - derived of GRAPPA a k-space based technique) and mSENSE (an image based enhanced version of SENSE).
| | | |  | | | | | | | | |  Further Reading: Further Reading: | | Basics:
|
|
News & More:
| |
| |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Coil' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
The quality factor (Q) applies to any resonant circuit component; most often the quality factor of the coil determines the overall Q of the circuit.
Inversely related to the fraction of the energy in an oscillating system lost in one oscillation cycle. Q is inversely related to the range of frequency over which the system will exhibit resonance.
In a parallel tuned circuit (such as used in a MR coil), the quality factor is defined as:
Q = vL/R
where L is the coil inductance, R is the circuit resistance, and v is the angular frequency.
Increasing quality factor results in improving the signal to noise ratio SNR by a factor √Q and also produces a sharper frequency response (decreased band width). The Q of a coil will depend on the circumstances under which it is measured, e.g. whether it is 'unloaded' (no patient) or 'loaded' (patient). | |  | |
• View the DATABASE results for 'Quality Factor' (2).
| | | | |
|  | |  |  |  |
| |
|

From GE Healthcare;
GE's Signa Contour/i system uses the innovations like K4 technology and real-time interactive imaging.
This compact magnet with wide-flare gantry obtains high patient comfort with low costs.
Device Information and Specification CLINICAL APPLICATION Whole body Head and body coil standard; all other coils optional; open architecture makes system compatible with a wide selection of coils Standard: SE, IR, 2D/3D GRE and SPGR, Angiography;; 2D/3D TOF, 2D/3D Phase Contrast;; 2D/3D FSE, 2D/3D FGRE and FSPGR, SSFP, FLAIR, optional: EPI, 2D/3D Fiesta, FGRET, Spiral2D 0.8 mm to 20 mm; 3D 0.1 mm to 5 mm 128x512 steps 32 phase encode POWER REQUIREMENTS 480 or 380/415 V STRENGTH SmartSpeed 23 mT/m, HiSpeed Plus 33 mT/m | |  | | | |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Coil' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|

From GE Healthcare;
The GE Signa HDx MRI system is a whole body magnetic resonance scanner designed to support high resolution, high signal to noise ratio, and short scan times.
The 1.5T Signa HDx MR Systems is a modification of the currently marketed GE 1.5T machines, with the main difference being the change to the receive chain architecture that includes a thirty two independent receive channels, and allows for future expansion in 16 channel increments. The overall system has been improved with a simplified user interface
and a single 23" liquid crystal display, improved multi channel surface coil connectivity, and an improved image reconstruction architecture known as the Volume Recon Engine (VRE).
Device Information and Specification CLINICAL APPLICATION Whole body CONFIGURATION Compact short bore Standard: SE, IR, 2D/3D GRE and SPGR, Angiography: 2D/3D TOF, 2D/3D Phase Contrast; 2D/3D FSE, 2D/3D FGRE and FSPGR, SSFP, FLAIR, EPI, optional: 2D/3D Fiesta, FGRET, Spiral, Tensor, 2D 0.7 mm to 20 mm; 3D 0.1 mm to 5 mm 128x512 steps 32 phase encode POWER REQUIREMENTS 480 or 380/415 less than 0.03 L/hr liquid helium | |  | | | |
|  |  | Searchterm 'Coil' was also found in the following services: | | | | |
|  |  |
| |
|
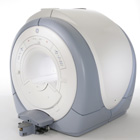
From GE Healthcare;
The Signa HDx MRI system is GE's leading edge whole body magnetic resonance scanner designed to support high resolution, high signal to noise ratio, and short scan times.
Signa HDx 3.0T offers new technologies like ultra-fast image reconstruction through the new XVRE recon engine, advancements in parallel imaging algorithms and the broadest range of premium applications. The HD applications, PROPELLER (high-quality brain imaging extremely resistant to motion artifacts), TRICKS (contrast-enhanced angiographic vascular lower leg imaging), VIBRANT (for breast MRI), LAVA (high resolution liver imaging with shorter breath holds and better organ coverage) and MR Echo (high-definition cardiac images in real time) offer unique capabilities.
Device Information and Specification CLINICAL APPLICATION Whole body
CONFIGURATION Compact short bore SE, IR, 2D/3D GRE, RF-spoiled GRE, 2DFGRE, 2DFSPGR, 3DFGRE, 3DFSPGR, 3DTOFGRE, 3DFSPGR, 2DFSE, 2DFSE-XL, 2DFSE-IR, T1-FLAIR, SSFSE, EPI, DW-EPI, BRAVO, Angiography: 2D/3D TOF, 2D/3D phase contrast vascular IMAGING MODES Single, multislice, volume study, fast scan, multi slab, cine, localizer H*W*D 240 x 2216,6 x 201,6 cm POWER REQUIREMENTS 480 or 380/415, 3 phase ||
COOLING SYSTEM TYPE Closed-loop water-cooled grad. | |  | | | |
|  | |  |  |
|  | | |
|
| |
 | Look
Ups |
| |